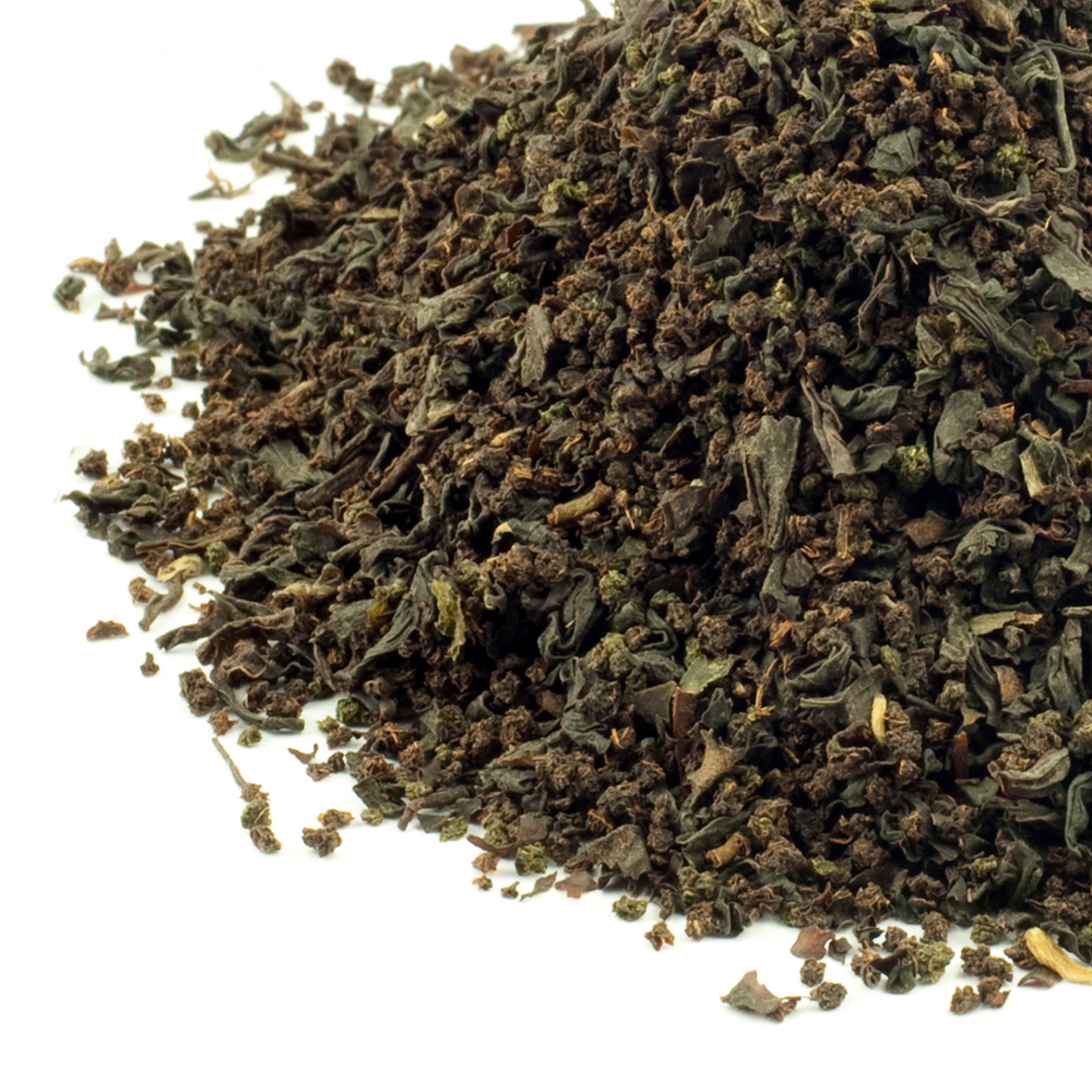
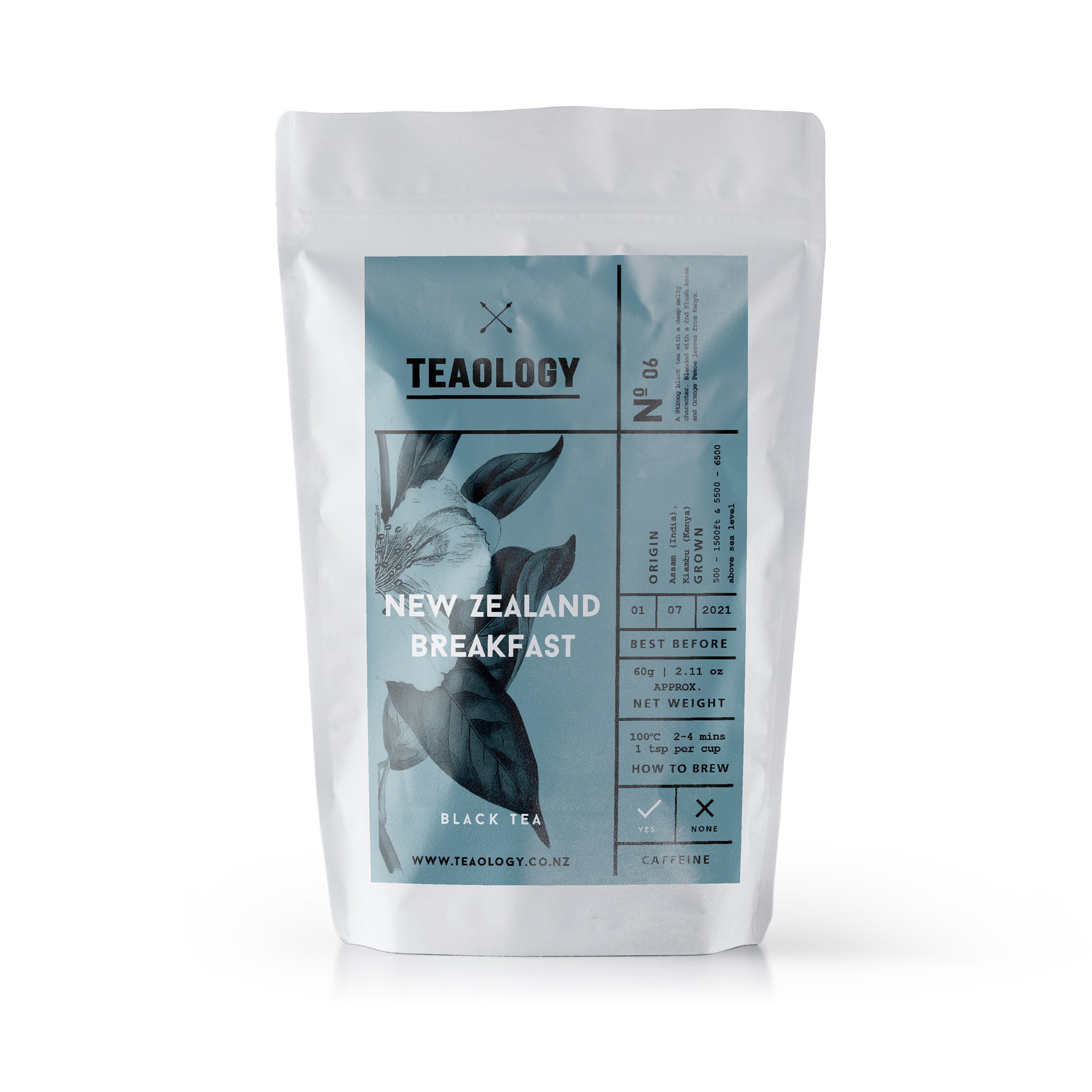
Kiwi Breakfast
By Teaology
If you like to start your day with a good strong cup of tea, this Kiwi Breakfast tea is just what you're looking for! A combination of high-quality teas from a 2nd Flush Assam and a February tea from Kenya gives this tea a kick start to your day.
BREWING RECOMMENDATION
1-2 teaspoons per cup with or without a dash of milk or squeeze of lemon
INGREDIENTS
Pure Black Tea
ORIGIN
Assam (India), Kiambu (Kenya).
ALTITUDE
(500 - 1500ft), (5500 - 6500) ft above sea level
Approx between 27- 35mg per cup
Makes 15 - 30 standard cups of tea depending on personal strength of brew
TEA-SER VIAL
Makes 5 - 10 standard cups of tea depending on personal strength of brew
Health Benefits
-
Antioxidants in Tea
Antioxidants are chemicals that naturally help fight the harmful oxidation effects of unstable molecules in your body called free radicals that occurs naturally in the body when you are exposed to harmful environmental factors. Free radicals have extra electrons around them that bombard the molecules of cell membranes which leads to cell damage. Antioxidants take up these extra electrons so that your cells don’t have to. Free radicals may come from environmental contaminants such as radiation, pollution and exposure to toxins; but they also form as a result of normal bodily processes such as breathing oxygen.
There are three primary types of antioxidants found in nature. These include phytochemicals, vitamins, and enzymes. Although black tea has high levels of some essential antioxidant enzymes and vitamins such as Magnesium and Folate is it the Phytochemicals in tea that make them so powerful.
Antioxidant Phytochemicals
Phytochemicals are the antioxidants that are naturally used by plants to protect themselves against free radicals . Studies show that humans who eat sources of phytochemicals also benefit from the antioxidant properties of the plant. Phytochemicals are broken down into the following categories:• Carotenoids
• Flavonoids
• Allyl sulfides
• PolyphenolsMain flavonoids of a living tea leaf
Flavonoids are secondary metabolites (a group of naturally occurring biochemicals) that help a plant to grow strong and attain its various biological characters, such as its smell, colour or self-defense. The amount and varieties differ in different plants and in different parts and growing stages of a plant. The most predominant flavonoids in a growing young tea leaf are:Catechins in tea
• Catechin, Epigallocatechin (EGC)
• Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG)
• Epicatechin (EC)
• Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECg, or ECG, or EC3G)Catechins protect cell DNA. They are anti-mutagenic, anti-inflammatory and anti-pathogenic all delivered in a cup of tea.
Of all the catechins, EGCG, is a unique catechin in tea, has repeatedly demonstrated itself as the most potent health contributive factor in tea. It accounts for 50~75% of the catechins in green teas.Once a tea leaf is plucked, its flavonoids very slowly undergo a process of enzyme triggered oxidation that cause them, in particular the catechins, to transform into various substances, some are other forms of flavonoids, some yet other substances that may influence the taste and aroma of the final product. The production of various categories of tea is largely based on the control of this oxidation phenomenon. This oxidation of catechins is called “fermentation” in the tea production process.
Flavonols in tea
• Kaempferol
• Myricetin
• QuercetinKaempferol:
Acts as an antioxidant by reducing oxidative stress. Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, cardioprotective, neuroprotective, antidiabetic, antiosteoporotic, estrogenic/antiestrogenic, anxiolytic, analgesic, and antiallergic activities. It has been linked with many sucessful anti-cancer treatments and and it is currently under consideration as a possible cancer treatment.Myricetin:
Myricetin works by disrupting cellular pathways. It interacts with enzymes and suppresses their activities (enzyme inhibition). Myricetin, is an anti-inflammatory, prevents blood clots, has many anti-cancer properties, increases glucose uptake thus helping manage diabetes, slows the progression of Alzheimers disease, protects the heart, controls fat deposition and helps prevent weight gain, anti-microbial, helps protect the skin against UV radiation and prevents skin wrinkles, protects eyesight and increases bone mass, Myricetin also increases iodine uptake as well as iodine retention by thyroid cells.Quercetin:
Inflammation is the root of most diseases, and Quercetin effectively fights anti-inflammatory related diseases such as: Atherosclerosis, circulation, high cholesterol, insulin resistance and diabetes, heart disease, eye-related disorders including cataracts, allergies, asthma and hayfever, stomach ulcers, cognitive impairment, gout, viral infections, inflammation of the prostrate, bladder and ovaries, chronic fatigue syndrome, cancer, chronic infections of the prostrate and skin disordersFlavones in tea
• Apigenin
• LuteolinApigenin:
Anti-inflammatory, antidepressant-like effects, anti-cancer properties, protects the heart, prevents bone loss, stimulates brain cell generation.Luteolin:
Luteolin interferes with nearly all types of cancer cells.
It inhibits the growth of new blood vessels in tumors, the metabolism of carcinogens, as well as stopping the progression of the cell cycle in cancer cells. Luteolin also induces cell death in cancer cells. Luteolin is also an anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, prevents UVB-induced skin aging, luteolin can be used in the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, protects the brain from neurological impairments, anti-viral properties, helps prevent cataracts, Luteolin has anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects which can reduce the effects of multiple sclerosis, Luteolin has anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects which can reduce the effects of multiple sclerosisFlavonoids in green tea
In the case of a fine green tea, the plucked leaf is withered very briefly for slight dehydration and then put through heat to halt the enzyme-triggered oxidation. The most original and quantity of flavonoids are thus kept. They can take up an average of 30% of the dry weight of the tea, dependent on the tea variety, pluck quality and harvest season. That means you have on average 300 mg of catechins and other flavonoids in each gram of tea leaves.Flavonoids in black tea
When the fresh leaves are taken to produce black tea, a large proportion of these flavonoids and catechins is oxidized to become other substances, mostly flavonoids of larger molecular structures, such as:• Theaflavins (TF)
• Thearubigins (TR)
• Theabrownins (TB)While most of medical researches on tea’s health potential focus around green tea catechins, in particular EGCG, there are a number done on theaflavins, finding that they may also be contributive to reduction of cardiovascular diseases and prevention of diabetes. Theaflavins contribute to the yellowish orange colour of the black tea infusion. They make up on average 6% of the black tea flavonoids.
Much fewer studies have been done on theabrownins, which are a lot more abundant in post-fermented teas, but with promising results on cholesterol control resulting in a reduced risk for heart disease. The antioxidants in green, black, and oolong teas can help block the oxidation of LDL (bad) cholesterol, increase HDL (good) cholesterol and improve artery function.
Drinking a cup of tea a few times a day helps to absorb antioxidants and other nutritional plant compounds. In green-tea drinking cultures, the usual amount is three cups per day. Allow tea to steep for three to five minutes to bring out its catechins. The best way to get the catechins and other flavonoids in tea is to drink it freshly picked and freshly brewed. Decaffeinated, bottled ready-to-drink tea (bag) preparations, and instant teas have less of these compounds.
Note that tea can impede the absorption of iron from fruits and vegetables. Adding lemon or milk or drinking tea between meals will counteract this problem.
-
Black Tea
The major difference between black tea and others is that it is fully oxidized. During the process of oxidation, catechins are converted into tannins, which are responsible for the color of black tea. Although the antioxidant composition of black tea differs from other less oxidized varieties, total antioxidant content after the oxidation process is similar to what it was before.
+ Stimulates metabolism and weight loss
+ Increases energy and blood flow without overstimulating the heart
+ UP to 10 times higher in Antioxidants than fruits and vegetables
+ Polyphenols which help prevent and reverse DNA damage
+ Polyphenol and catechins helps prevent against some cancers
+ Phytochemicals helps strengthen bones
+ Amino acid L-theanine aids relaxation and concentration
+ Tannins improves digestive tract
+ Contains alkylamine antigens that improve the immune system
+ Helps prevent arthritis
+ Lowers risk of developing type 2 diabetes
+ Stimulates the respiratory system and the kidneys
+ Helps reduce high cholesterol
+ Prevents tooth Decay
A Better Heart
Regardless of people’s country of origin recent research shows that individuals who consume 3 or more cups of tea had a 21% lower risk of a stroke than people who consume less than 1 cup of green or black tea per day. While, thanks to the Bioflavonoids present in tea the consumption of at least four to five cups of tea per day helps also lower total cholesterol levels and reduce the cholesterol’s ability to form plaques in arteries and may promote blood vessel relaxation in those with coronary artery disease or high cholesterol.DNA Repair
Black tea contains a range of antioxidant sub-groups, one of which being polyphenols, which help block and repair DNA damage associated with exposure to harmful environmental factors such as radiation and toxic chemicals. The antioxidants contained in tea are different from those obtained from fruits and vegetables and therefore, as a regular part of your diet they can provide additional benefits towards a healthy lifestyle.Cancer Prevention
Many researches now suggest that the high levels of antioxidants like polyphenol and catechins in tea may help prevent some types of cancer. Tea also contains Bioflavonoids
which are polynutrients, they are converted to plant estrogens, or phytoestrogens, which help inhibit the growth of hormone-dependent cancers.Healthy Bones
Regular tea drinkers have stronger bones and lower probability of developing arthritis due to the high amounts of phytochemicals found in tea.Lower Risk of Diabetes
Black tea tea helps regulate glucose levels by slowing the rise of blood sugar after eating. It lowers blood sugar levels by blocking the enzyme that turns starch into glucose. This is similar to some drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes. It also slows down absorption of sugar in the small intestine. This can prevent high insulin spikes and resulting fat storage.
Based on a research study conducted by elderly people living in the Mediterranean islands it was discovered that people that had been consuming black tea on a long-term basis on a moderate level (i.e. 1-2 cups a day) had a 70% lower chance of having or developing type 2 diabetes.Stress Relief
We all are aware and well experienced about the calming and relaxing benefits of black tea. Not only does it help slow you down after a long day, studies show that the amino acid L-theanine found in black tea can help you relax and concentrate better. Black tea has also been shown to reduce levels of the stress hormone cortisol when consumed in moderate amounts on a regular basis.Better Immune System
Black tea contains alkylamine antigens that help boost our immune response. In addition, it also contains tannins that have the ability to fight viruses and hence keep us protected from influenza, stomach flu and other such commonly found viruses in our everyday lives. Tea also contains Bioflavonoids which is a type of polynutrient. In the body, the Bioflavanoids are converted to plant estrogens, or phytoestrogens,which aid the immune system by protecting the body’s cells against environmental pollutants.Healthy Digestive Tract
In addition to improving your immune system, tannins also have a therapeutic effect on gastric and intestinal illnesses and also help decrease digestive activity.Increased Energy
Unlike other drinks that have a relatively higher caffeine content, caffeine found in tea can help enhance blood flow to the brain without overstimulating the heart. It also stimulates the metabolism and respiratory system, as well as the heart and the kidneys.Dizziness
Black tea can help prevent orthostatic hypertension (dizziness caused by standing too quickly).Prevents Tooth Decay
Black tea also contains enough fluoride to possibly help prevent dental carries. Compounds also found in black tea are capable of killing or suppressing growth and acid production of cavity causing bacteria in dental plaque. Black tea also affects the bacterial enzyme glucosyltranferase which is responsible for converting sugars into the sticky matrix material that plaque uses to adhere to teeth. In addition, certain plaque bacteria, upon exposure to black tea, lost their ability to form the clumpy aggregates with other bacteria in plaque, thereby reducing the total mass of dental plaque. Black tea also helps combat two types of bacteria – Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus that are both associated with tooth decay and gum disease.